
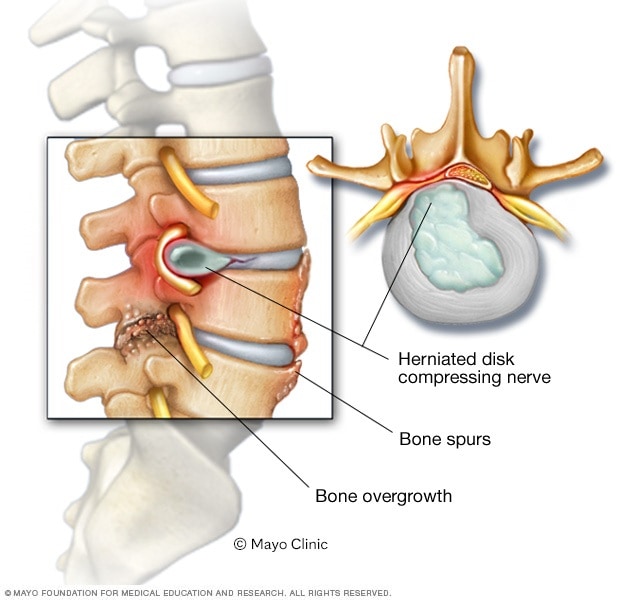
When this canal narrows, a nerve could become pinched or trapped, resulting in chronic pain and symptoms.Cervical spinal stenosis is a nerve compression problem in your neck. The foraminal canal is a small passageway on either side of the vertebrae that allows nerves to exit the spine. Cervical foraminal narrowing is the narrowing of the foraminal canal in the cervical spine.
To compensate for this increased bone loss, the body produces enlarged bones that are substandard in quality. Paget’s Disease: Paget’s disease results from an imbalance in bone remodeling, in which the rate of bone breakdown—a natural, ongoing process—overtakes the rate of bone reconstruction. As abnormal cells multiply, the spinal cord may suffer compression, amplifying pain signals that shoot into the arms and legs. Spinal Tumors: Spinal tumors create obstructions in the spinal canal. Spondylolisthesis (Slipped Vertebra): When a vertebra slides forward out of alignment—whether from arthritic changes in the spine or sudden injury—the dislocated vertebral body can cause spinal stenosis by applying undue pressure to the spinal cord. For example: Ligaments that reinforce the spine may thicken osteoarthritis may cause bony protrusions—known as bone spurs—to develop on the vertebrae or facet joints of the spine and, intervertebral discs may lose their shape and balloon outward, herniating (or rupturing) as the mounting internal pressure becomes too intense.As bones grow, ligaments thicken, and intervertebral discs swell, your spinal cord loses its natural real estate and may become painfully crushed or pinched—by the very anatomy that serves to protect it!Additional causes of spinal stenosis may include:
Sciatica: White-hot, electric, or stabbing pain that emanates from the sciatic nerve in the lower back and spreads downward through the hips, buttocks, legs, or feet occurs commonly with lumbar (i.e. Pinched Nerve Pain: Searing pain that discharges from the region of spinal nerve compression and builds in intensity as it travels down through the limbs Although the severity of spinal stenosis may vary from a mild annoyance to an incapacitating burden, common symptoms may include: Frazier, has devoted his life to identifying minimally invasive surgical solutions that are effective for restoring spine health!Because your spinal cord is responsible for regulating movement, balance, and sensation, spinal stenosis often renders walking painful or impossible, disrupts balance, and results in tingling or loss of sensation in the extremities. Spinal Trauma: Vehicular or motorcycle accidents high-impact sports or sudden, severe falls can dislodge spinal vertebrae or produce shards of bone that penetrate into the spinal column.Do your symptoms of nerve pain—the tingling, numbness, and loss of balance or motor skills—sound like spinal stenosis? Our Harvard-trained and internationally recognized surgeon, Dr.
Global Balance Disturbances: Loss of balance or weakening of gross motor skills that coordinate walking or moving the arms and legs Paresthesia: Numbness, tingling, or pins-and-needles sensations that assail the extremities Pain while Walking: Also known as claudication, spinal stenosis can cause severe pain that interferes with walking claudication is often only alleviated by sitting or bending forward at the waist to relieve nerve compression The neck) and migrates downward through the shoulders, arms, hands, and fingertips Cervical Radiculopathy: Throbbing or scorching pain that stems from the site of spinal stenosis in the cervical spine (i.e.
Foraminotomy: A foraminotomy is a minimally invasive surgical solution to eliminate foraminal stenosis—a subtype of spinal stenosis in which spinal nerve compression occurs at the foramina. This same-day procedure boasts faster recovery times and less postoperative pain than “traditional” methods. Artificial Disc Replacement: This minimally invasive surgical procedure corrects spinal stenosis by extracting and replacing a damaged intervertebral disc with a more durable, artificial model. This effective outpatient procedure is often regarded as the benchmark against which all other lumbar decompression surgeries are compared. Minimally Invasive Laminectomy: This technique involves pressure-relieving removal of the lamina (or backside of a vertebra) to broaden the spinal canal and reverse spinal stenosis.
Frazier tailors each of his procedures to optimize a patient’s recovery time and to minimize post-operative pain. Dedicated to providing the highest quality of patient-centered care, Dr. Frazier evaluates the needs of each of his patients on an individual basis. During a foraminotomy, your surgeon excises overgrown bone or inflamed tissues that block the foramina and impinge upon spinal nerves.Although these techniques represent three of the most popular surgical interventions to correct spinal stenosis, Dr.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
